Innovating tools for solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Our group has been paving the way for important innovations in solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In constrast to traditional, carbon-detected methods, proton detection has revolutionized the field. Based on work with Prof. Dr. Bernd Reif during his PhD, Rasmus has been interested in pushing proton detection further and further over the years. We have created new approaches for shift assignments, structure calculation, protein dynamics, as well as interactions between proteins and small molecules or water.
Spectroscopic tools that we have introduced or further developed are, for example:
|
Paramagnetism for accelated acquisition and elucidation of protein surfaces and structure |
|
|
|
R. Linser, V. Chevelkov, A. Diehl, B. Reif, “Sensitivity Enhancement Using Paramagnetic Relaxation in MAS Solid-State NMR of Perdeuterated Proteins”, J. Magn. Reson. 189, 209–216 (2007).
R. Linser, U. Fink, B. Reif, “Probing Surface Accessibility of Proteins Using Paramagnetic Relaxation in MAS solid-state NMR Spectroscopy”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (38), 13703–13708 (2009). P. Rovó, K. Grohe, K. Giller, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Proton Transverse Relaxation as a Sensitive Probe for Structure Determination in Solid Proteins”, ChemPhysChem,, 16 (18), 3791–3796 (2015). |
|
Innovative pulse sequences for resonance assignments, introducing protons as detection nucleus, INEPTs for magnetization transfer, sequences correlating whole sets of carbon shifts with the amide backbone, and many more |
|
 |
R. Linser, M. Dasari, U. Fink, P. Schmieder, J.-M. Lopez del Amo, S. Marcovic, M. Hiller, H. Oschkinat, D. Oesterheld, B. Reif, “Proton detected solid state NMR of fibrillar and membrane proteins”, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 50 (19), 4508–4512 (2011); R. Linser, “Backbone Assignment of Perdeuterated Proteins Using Long-Range H/C-Dipolar Transfers”, J. Biomol. NMR 52 (2), 151–158 (2012). R. Linser, “Sidechain to backbone correlation in perdeuterated proteins through combined excitation and long-range magnetization transfer.”, J. Biomol. NMR 51 (3), 221–226 (2011). N. Kulminskaya, S. K. Vasa, K. Giller, S. Becker, A. Kwan, M. Sunde, R. Linser, “Access to side-chain carbon information in deuterated solids under ultra-fast MAS through non-rotor-synchronized mixing”, ChemComm, 52 (2), 268-271 (2016). S. Xiang, K. Grohe, P. Rovó, S. K. Vasa, K. Giller, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Sequential backbone assignment based on direct amide-to-amide correlation experiments”, J. Biomol. NMR, 62 (3), 303–311 (2015). |
|
Higher-dimensionality approaches |
|
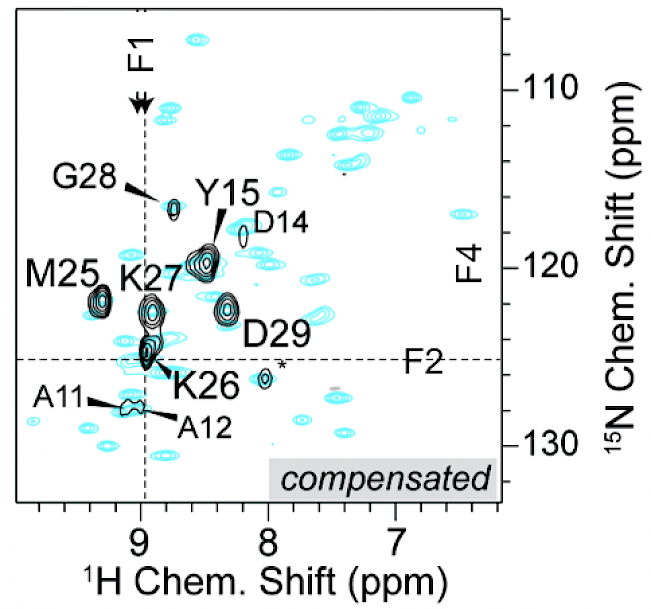 |
R. Linser, B. Bardiaux, S. G. Hyberts, A. Kwan, V. Morris, M. Sunde, G. Wagner, “Solid-State NMR Structure Determination from Diagonal-Compensated, Sparsely Nonuniform-Sampled 4D Proton–Proton Restraints”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 (31), 11002–11010 (2014). S. Xiang, J. Biernat, E. Mandelkow, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Backbone assignment for minimal protein amounts of low structural homogeneity in the absence of deuteration”, Chem. Commun., 52, 4002-4005 (2016). A. Klein, S. K. Vasa, R. Linser, “Automated projection spectroscopy in solid-state NMR, J. Biomol. NMR 72, 163-170 (2018). S. K. Vasa, H. Singh, P. Rovó, R. Linser, “Dynamics and interactions of a 29-kDa human enzyme studied by solid-state NMR”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 9, 1307−1311 (2018). (Link) |
|
Characterization of ensemble characteristics within solid protein samples |
|
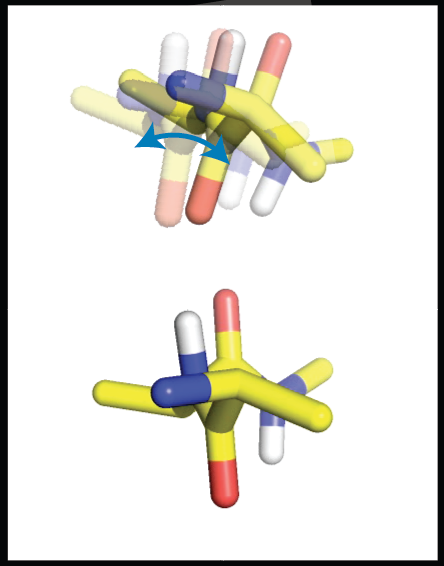 |
S. Xiang, N. Kulminskaya, B. Habenstein, J. Biernat, K. Tepper, M. Paulat, C. Griesinger, S. Becker, A. Lange, E. Mandelkow, R. Linser, “A two-component adhesive: Tau fibrils arise from a combination of a well-defined motif and conformationally flexible interactions”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 139, 2639−2646 (2017). E. Burakova, A. Klein, S. K. Vasa, R. Linser, “Non-uniform sampling in quantitative assessment of heterogeneous solid-state NMR line shapes”, J. Biomol. NMR, 74, 71–82, DOI: 10.1007/s10858-019-00291-z (2020). (Link) |
|
Access to H/D exchange in solid preparations over time |
|
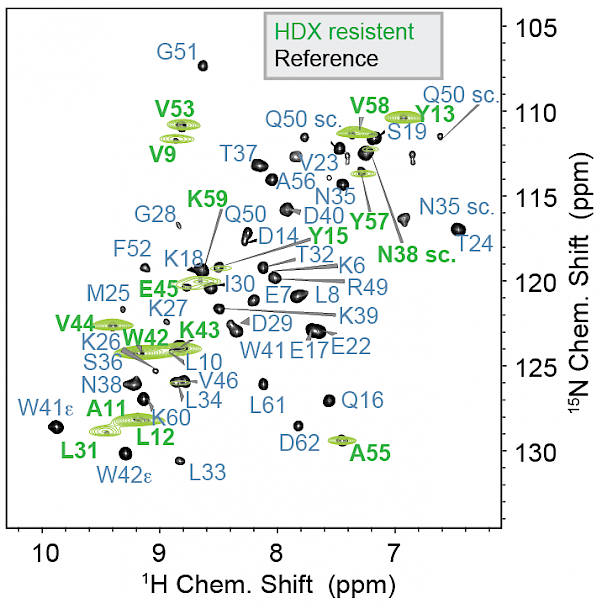 |
K. Grohe, K. Tekwani Movellan, S. K. Vasa, K. Giller, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Non-equilibrium hydrogen exchange for determination of H-bond strength and water accessibility in solid proteins”, J. Biomol. NMR, 68 (1), 7-17 (2017). |
|
Approaches towards proton-detected solid-state NMR with non-deuterated samples |
|
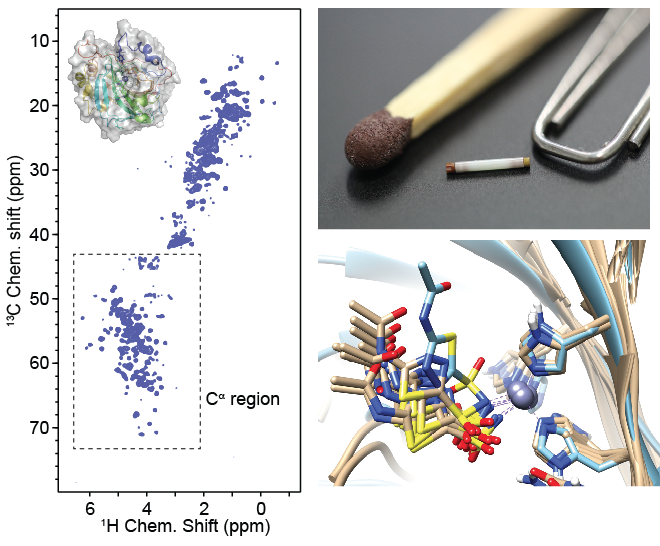 |
S. K. Vasa, P. Rovó, K. Giller, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Access to Aliphatic Protons as Reporters in Non-Deuterated Proteins by Second-Order Transfer”, PhysChemChemPhys, 18, 8359 – 8363 (2016). S. Xiang, J. Biernat, E. Mandelkow, S. Becker, R. Linser, “Backbone assignment for minimal protein amounts of low structural homogeneity in the absence of deuteration”, Chem. Commun., 52, 4002-4005 (2016). S. K. Vasa, H. Singh, K.Grohe, R. Linser, "Assessment of a large enzyme-drug complex by proton-detected solid-state NMR without deuteration", Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., DOI: 10.1002/anie.201811714 (2019). (Link) (Cover article: See the picture here!) |
Overview articles:
S. K. Vasa, P. Rovó, R. Linser, “Protons as versatile reporters in solid-state NMR spectroscopy”, Acc. Chem. Res., 51 (6), 1386-1395 (2018). (Link)
R. Linser, “Solid-state NMR spectroscopic trends for supramolecular assemblies and protein aggregates”, invited “Trends” article in Solid state Nucl. Magn. Res., 87:45-53 (2017).
R. Linser, R. Sarkar, A. Krushelnitzky, A. Mainz, B. Reif, “Dynamics in the Solid State: Perspectives for the Investigation of Amyloid Aggregates, Membrane Proteins, and Soluble Protein Complexes”, J. Biomol. NMR 59 (1), 1–14 (2014).